|
What is a
contaminated site?
Who does
what?
Why is it important?
What is risk management?
Risk assessment
fundamentals
Risk assessment
methods
Limitations
of risk assessment
What are RA tiers?
Initiation
Problem Identification
Receptor
Characterisation
Exposure Assessment
Toxicity Assessment
Information
Terrestrial Benchmark Values
Aquatic Benchmark Values
Risk
Characterisation
RM Decisions
Glossary
FAQ's
|
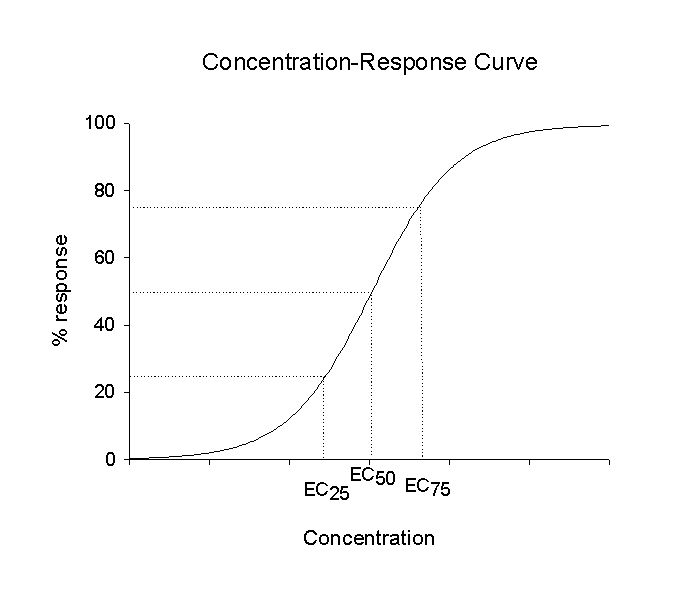
Measures of the level (i.e., concentration or dose) of a chemical stressor at
which a specific level of toxicity is observed in a receptor (eg LC50).
Toxicity values are determined by the exposure - effect relationship
generated in toxicity tests, and are generally expressed as the concentration(s)
or dose(s) that evoke a specific effect (in the measurement end point) over a
fixed exposure duration. An example of a concentration - response curve is given
below.
Toxicity values are derived from toxicity tests which are usually conducted
on one or more species. Toxicity data may be derived from single chemical
exposures or by testing samples of material removed from the contaminated site.
In ecotoxicological assessments, toxicity tests may measure lethal or sublethal end points, as
long as the endpoint measured can be related to an ecologically relevant impact.
Examples of commonly reported toxicity values are:
- LD or LC Lethal Dose or Lethal Concentration
- the dose or concentration which produces a specified level of
mortality in the test population within a specified time, eg LC50
is the median lethal concentration or the concentration of a substance
at which 50% of the test population are killed. Typical levels are LC10,
LC25, LC50, LC75, LC100.
- ED or EC Effective Dose or Effective Concentration -
the dose or concentration that produces a specified level of effect in
the test population within a specifed time, eg EC50 is median
effective concentration or the concentration of a substance at which 50%
of the test population are affected. Typical levels are EC10,
EC25, EC50, EC75, EC100.
- NOEC No observable effect concentration
- LOEC Lowest observable effect concentration
|
![]()
